Understanding the Reverse Logistics Process: A Key to Sustainable Supply Chains
In today’s fast-paced and consumer-driven world, businesses are constantly seeking ways to optimize operations, cut costs, and enhance sustainability. One crucial yet often overlooked component of supply chain management is the reverse logistics process. Unlike traditional logistics that focuses on moving goods from manufacturers to consumers, reverse logistics is all about moving items in the opposite direction — from customers back to sellers or manufacturers.
This process plays a vital role in transportation and logistics, especially as companies face growing pressure to handle product returns, repairs, recycling, and disposal efficiently. In this blog, we’ll break down the reverse logistics process, its benefits, challenges, and how businesses can implement it successfully.
What Is Reverse Logistics?
Reverse logistics refers to the process of moving goods from their final destination back to the manufacturer or a third-party handler for return, repair, recycling, or disposal. It’s the opposite of traditional logistics, which involves delivering products from the producer to the consumer.
In simpler terms, reverse logistics answers the question:
“What happens to a product after the customer no longer needs it?”
Some common examples include:
- Returning damaged or defective products to manufacturers.
- Refurbishing or remanufacturing used items.
- Recycling packaging materials or electronics.
- Managing product recalls.
- Disposing of expired goods safely
The Role of Reverse Logistics in Transportation and Logistics
Reverse logistics is deeply intertwined with transportation and logistics operations. While forward logistics focuses on efficiency in delivery and distribution, reverse logistics emphasizes efficiency in retrieval and reprocessing.
Here’s how it connects:
- Transportation networks must be flexible enough to handle both deliveries and returns.
- Warehousing operations must accommodate returned items for inspection, sorting, or repair.
- Data management systems must track the flow of goods backward to ensure accountability and visibility.
A well-structured reverse logistics process allows companies to close the supply chain loop, promoting sustainability and maximizing asset recovery.
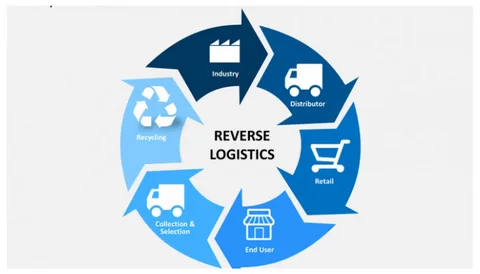
The Step-by-Step Reverse Logistics Process
Implementing an effective reverse logistics process involves several key stages. Let’s break it down:
1. Product Return Initiation
The process begins when a customer decides to return a product. This can occur for various reasons — defects, wrong size, dissatisfaction, or end-of-life recycling. Businesses must ensure a smooth return policy and efficient communication system to make this step customer-friendly.
2. Collection and Transportation
Once a return is initiated, the product needs to be collected and transported back to a warehouse, distribution center, or manufacturer. This step involves coordination between transportation and logistics teams to manage cost-effective return routes and minimize handling delays.
3. Inspection and Sorting
At the return center, items are inspected for quality and categorized based on their condition. Some items might be:
- Resellable as new or open-box items.
- Repairable or refurbishable.
- Recyclable for parts or materials.
- Unsuitable for reuse and require disposal.
4. Processing and Remanufacturing
Products deemed suitable for reuse often undergo repair, refurbishment, or remanufacturing. For example, in the electronics industry, defective devices can be repaired and resold at discounted rates.
5. Recycling and Disposal
For products that cannot be reused, recycling ensures that valuable materials such as metals, plastics, or glass are extracted. Non-recyclable waste is disposed of responsibly to reduce environmental impact.
6. Data Analysis and Reporting
Finally, data from returns and repairs are analyzed to identify trends, such as recurring product defects or inefficiencies in shipping. This helps companies improve future product design and logistics performance.
Benefits of a Strong Reverse Logistics System
A well-managed reverse logistics process brings numerous benefits to businesses and the environment alike:
1. Cost Savings
Recovering and reusing products or parts reduces the need for raw materials and manufacturing, saving costs in the long run.
2. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Efficient and hassle-free return processes improve customer trust and loyalty. Consumers are more likely to buy again if they know returns are easy and reliable.
3. Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness
By promoting recycling and reusing materials, companies contribute to a circular economy, reducing waste and their carbon footprint.
4. Better Inventory Management
Returned items that can be refurbished or resold help maintain inventory balance, reducing storage costs and overproduction.
5. Brand Reputation
Companies that prioritize environmental responsibility and transparency through reverse logistics often enjoy a stronger brand image and consumer goodwill.
Challenges in Reverse Logistics
Despite its benefits, reverse logistics comes with certain challenges:
- Complex Return Routes: Managing transportation for returns can be logistically difficult and costly.
- Quality Control: Determining which items are reusable requires time and skilled inspection.
- Data Inconsistencies: Tracking returned goods in real-time can be difficult without modern software systems.
- Storage and Handling Costs: Returned products often require separate facilities and processes.
- Environmental Regulations: Companies must comply with local recycling and disposal laws.
Overcoming these challenges requires technology integration, clear policies, and collaboration between supply chain partners.
Best Practices for Optimizing the Reverse Logistics Process
To make reverse logistics more efficient and cost-effective, businesses can adopt the following strategies:
1. Use Advanced Tracking Technology
Implementing RFID tags, IoT devices, and logistics management software enhances visibility across the supply chain.
2. Partner with Reliable Transportation Providers
Work with experienced transportation and logistics companies that specialize in handling returns efficiently and sustainably.
3. Automate Return Management
Use automated systems for processing returns, issuing refunds, and updating inventory to save time and reduce errors.
4. Promote Eco-Friendly Disposal
Partner with certified recycling centers and ensure proper disposal of non-reusable materials.
5. Analyze and Improve Continuously
Regularly review reverse logistics data to identify areas for improvement and adapt to customer feedback.
The Future of Reverse Logistics
As sustainability and customer convenience become top business priorities, reverse logistics is set to play an even greater role in global supply chains. The rise of e-commerce has also amplified the need for efficient return handling and product recovery. Companies investing in digital solutions and sustainable transportation and logistics strategies are already gaining a competitive edge.
Conclusion
The reverse logistics process is more than just handling returns — it’s a powerful tool for reducing waste, improving sustainability, and enhancing customer satisfaction. By integrating reverse logistics with efficient transportation and logistics practices, businesses can not only cut costs but also contribute positively to the environment and build long-term trust with their customers.
A smart reverse logistics strategy is no longer optional — it’s essential for every business aiming for sustainability, profitability, and customer loyalty.